Three reactions that include compound M (see Problem 62) are described here. Answer the questions that follow.
Question:
Three reactions that include compound M (see Problem 62) are described here. Answer the questions that follow.
(a) Treatment of M with catalytic amounts of acid in ethanol solvent causes isomerization to compound N: UV λmax(ϵ) = 241(17,500) and 310(72) nm. Propose a structure for N.
(b) Hydrogenation of compound N (H2 – Pd, ether solvent) produces compound J (Problem 62). Is this the result that you would have predicted, or is there something unusual about it?
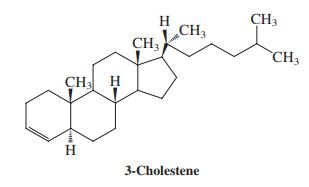
(c) Wolff-Kishner reduction of compound N (H2NNH2, H2O, HO-, Δ) leads to 3-cholestene. Propose a mechanism for this transformation.
Data From Problem 62
In 1862, it was discovered that cholesterol is converted into a new substance named coprostanol by the action of bacteria in the human digestive tract. Make use of the following information to deduce the structure of coprostanol. Identify the structures of unknowns J through M as well.
(i) Coprostanol, upon treatment with Cr(VI) reagents, gives compound J, UV λmax(ϵ) = 281(22) nm and IR = 1710 cm-1.
(ii) Exposure of cholesterol to H2 over Pt results in compound K, a stereoisomer of coprostanol. Treatment of K with the Cr(VI) reagent furnishes compound L, which has a UV peak very similar to that of compound J, λmax(ϵ) = 258(23) nm, and turns out to be a stereoisomer of J.
(iii) Careful addition of Cr(VI) reagent to cholesterol produces M: UV lmax(e) 5 286(109) nm. Catalytic hydrogenation of M over Pt also gives L.
Step by Step Answer:

Organic Chemistry structure and function
ISBN: 978-1429204941
6th edition
Authors: K. Peter C. Vollhardt, Neil E. Schore





