In the discussion of the Lindemann mechanism, it was assumed that the rate of activation by collision
Question:
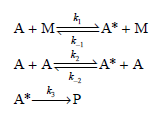
a. Demonstrate that the rate law expression for this mechanism is
![k;(k[A][M] + k,[A]) K[AJ) k1[M] + k_q[A] + k_3 R =](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1526/4/6/3/6965afbfcd0016621526463658616.jpg)
b. Does this rate law reduce to the expected form when [M] = 0?
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Question Posted:





