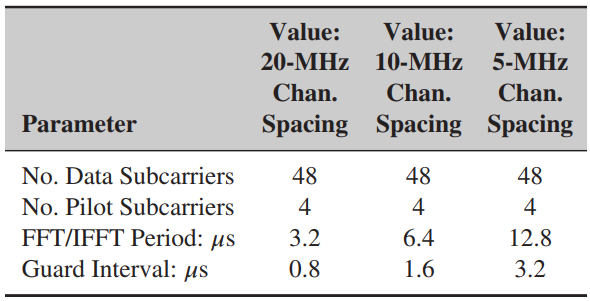
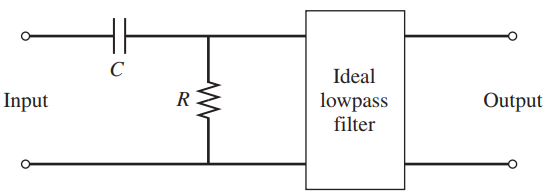
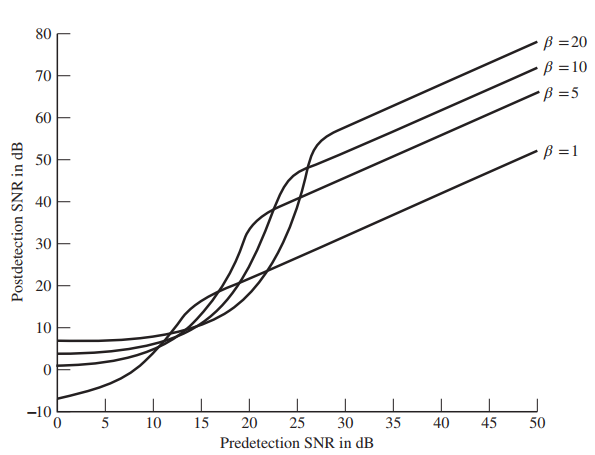
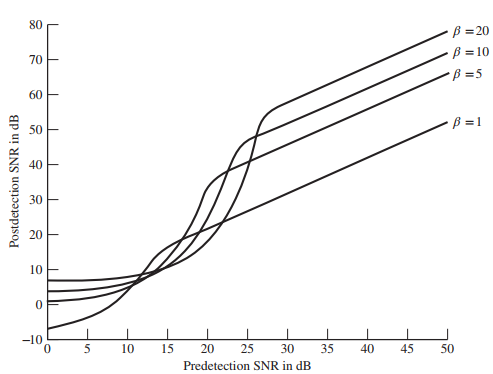
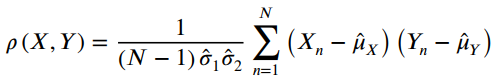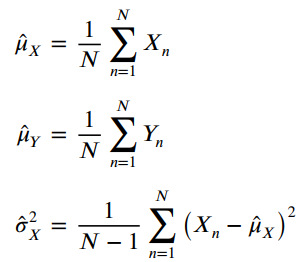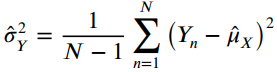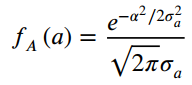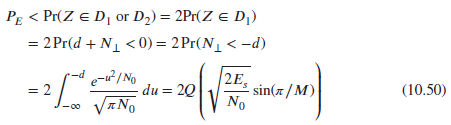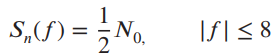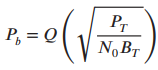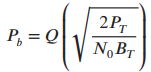![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


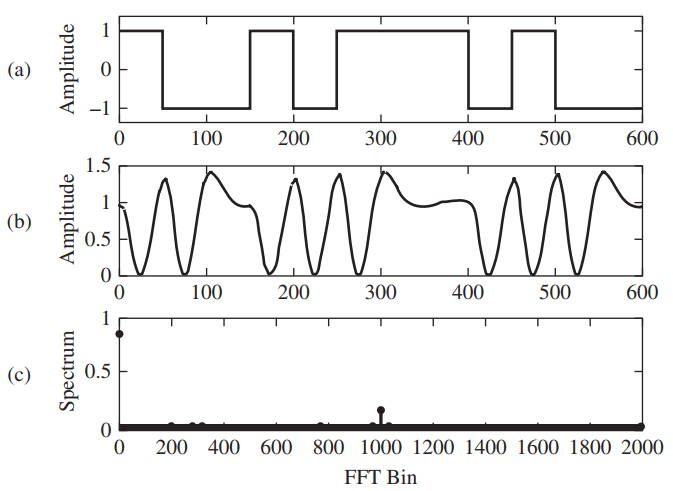
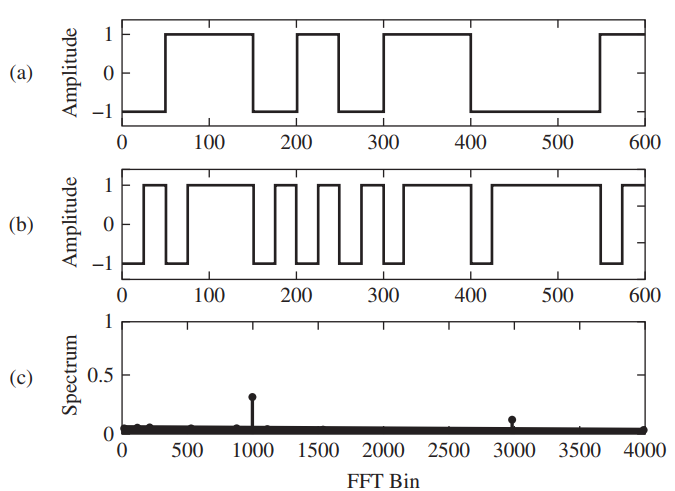
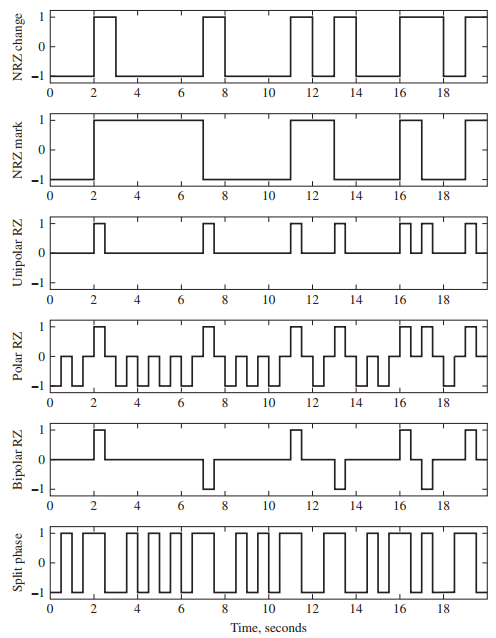
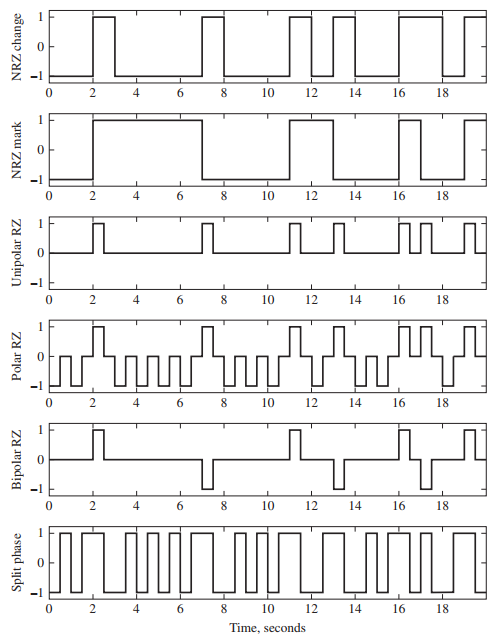
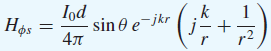
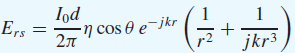
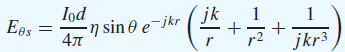
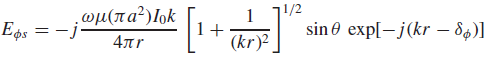
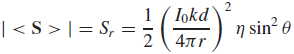
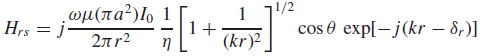
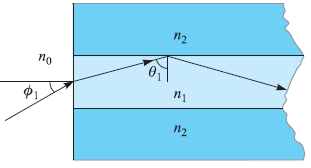
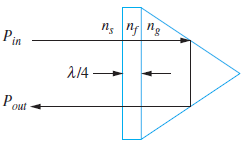
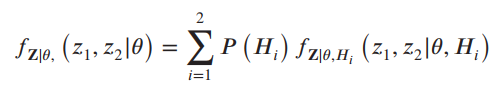
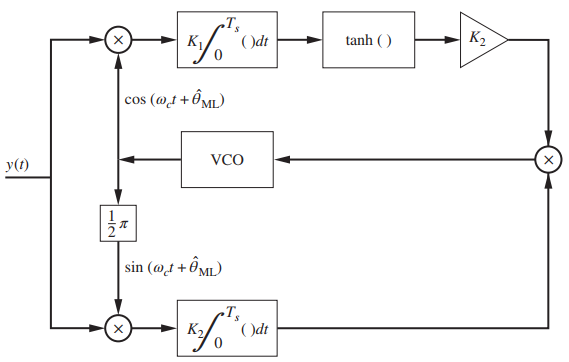
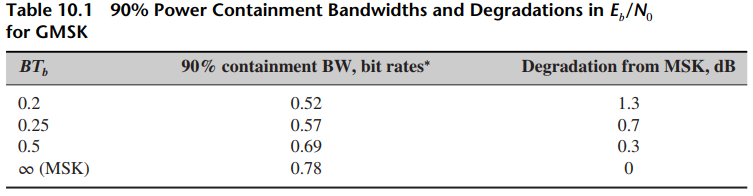
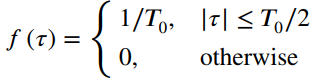
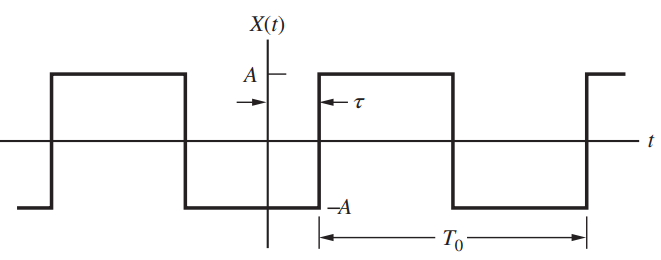
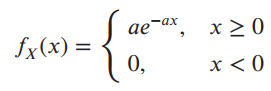
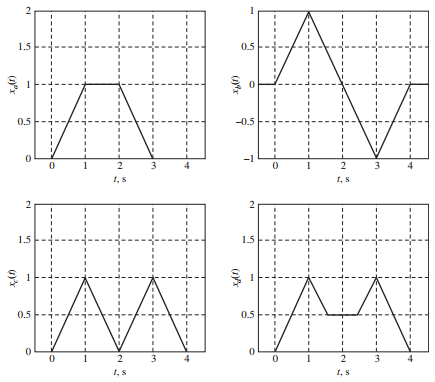
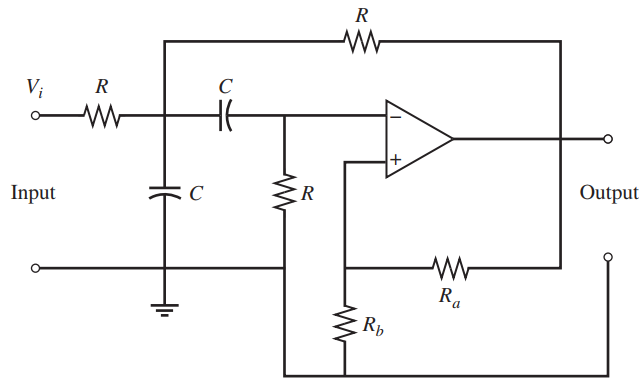
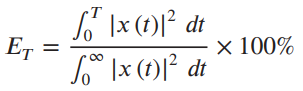
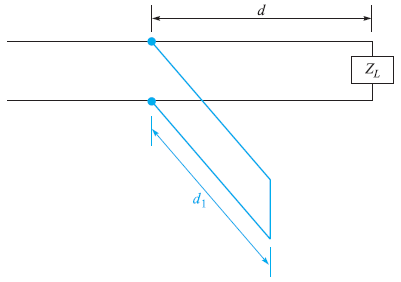
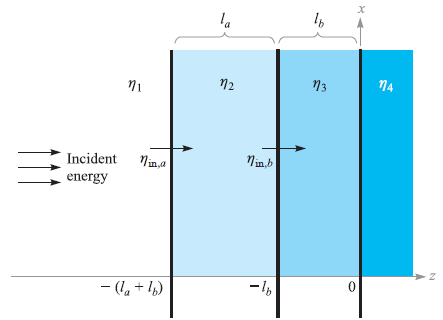
![[Po/(6e0)][3a? – r²] (r<a) V(r) = (a³ po)/(3eor) (r style=](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1536/4/0/4/6005b93ac78b878e1536386935717.jpg)