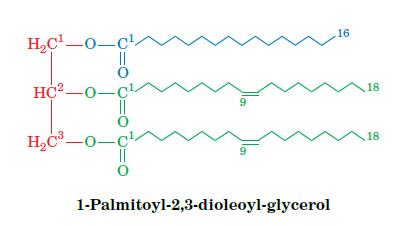
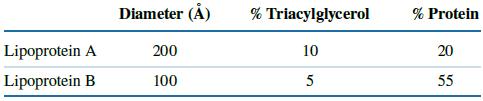
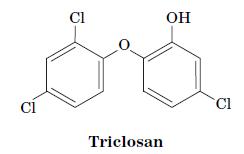
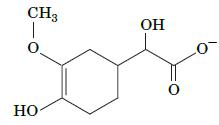
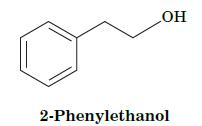
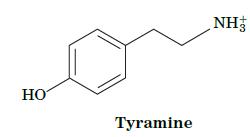
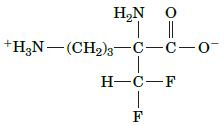
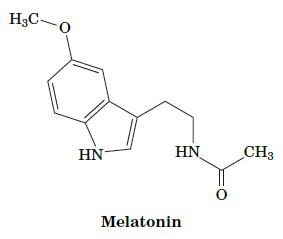
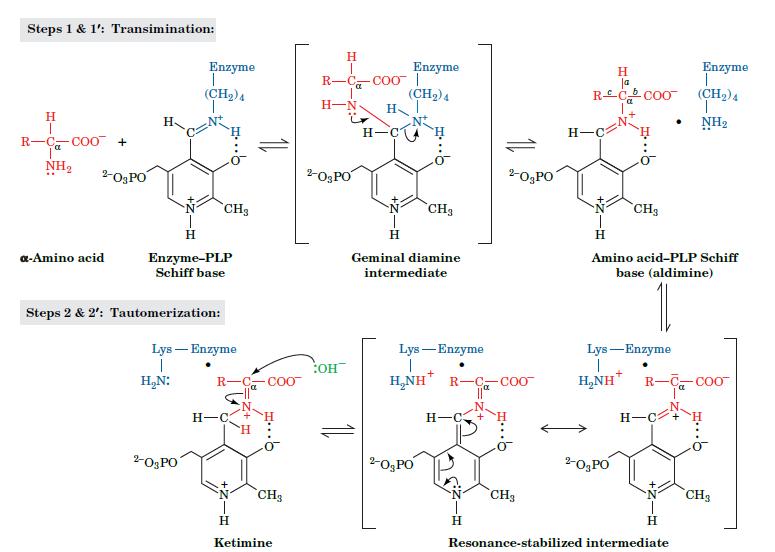
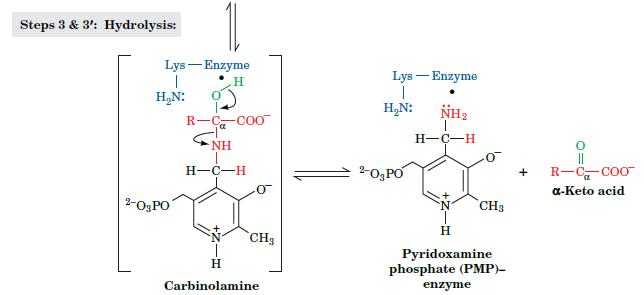
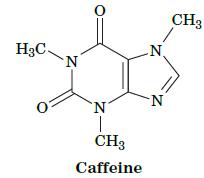
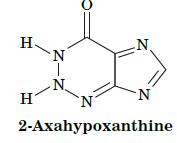
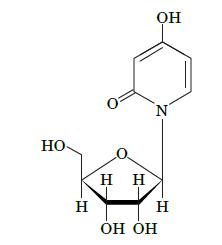
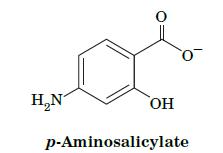
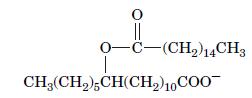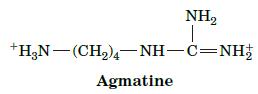Fundamentals Of Biochemistry Life At The Molecular Level 5th Edition Donald Voet, Judith G Voet, Charlotte W Pratt - Solutions
Explore the comprehensive solutions for "Fundamentals Of Biochemistry Life At The Molecular Level 5th Edition" by Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, and Charlotte W. Pratt. Access an exclusive online answers key, complete with solved problems and step-by-step answers. Our solution manual and solutions PDF provide detailed chapter solutions and a robust test bank for thorough understanding. Whether you're seeking questions and answers or an instructor manual, our resources offer everything you need to excel. Enjoy the convenience of a free download for your textbook needs, ensuring you have all the tools for academic success.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()