Malonic acid has two carboxylic acid groups and consequently undergoes two ionization reactions. The pK a for
Question:
Malonic acid has two carboxylic acid groups and consequently undergoes two ionization reactions. The pKa for the first ionization of malonic acid is 2.86; the pKa for the second is 5.70. The pKa of acetic acid is 4.76.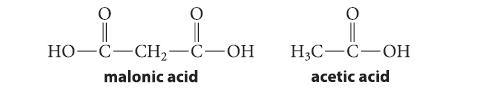
(a) Write out the equations for the first and second ionizations of malonic acid, and label each with the appropriate pKa value.
(b) Describe the ionization state of malonic acid if a solution of the acid is adjusted to pH 4.3 with NaOH.
(c) Use your answer to part (b) to determine the number of moles of base per mole of malonic acid required to adjust a solution of malonic acid to pH = 4.3.
(d) Why is the first pKa of malonic acid much lower than the pKa of acetic acid, but the second pKa of malonic acid is much higher than the pKa of acetic acid?
(e) Malonic acid is one member of a homologous series of unbranched dicarboxylic acids, so-called because they have two carboxylic acid groups. Compounds in this series have the following general structure.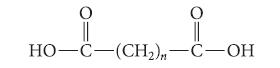
How would you expect the difference between the first and second pKa values to change as n increases? Explain.
Step by Step Answer:






