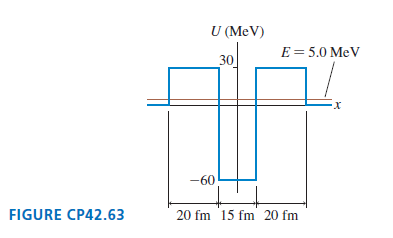
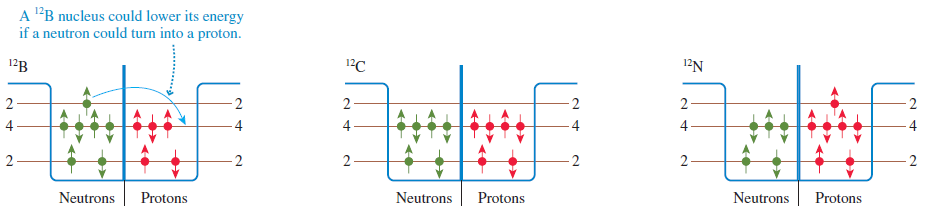
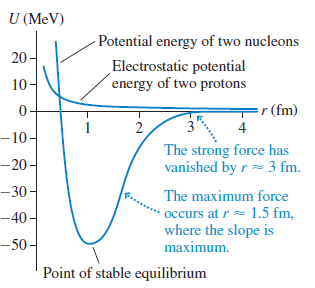
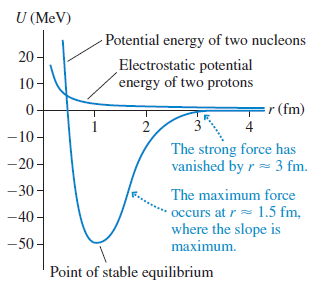
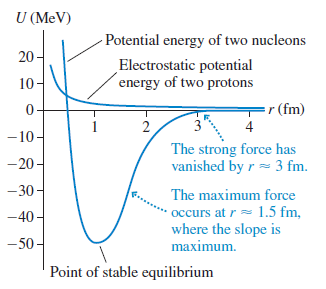
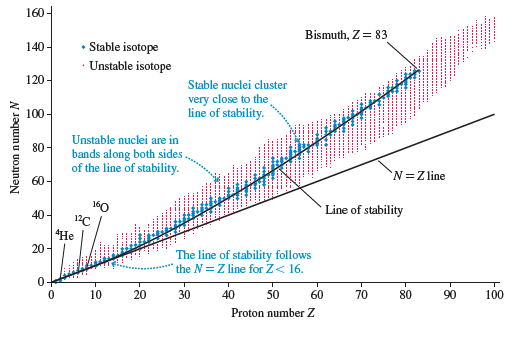
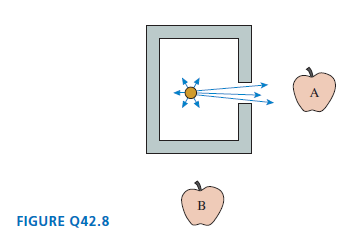
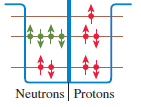
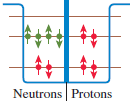
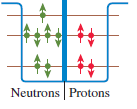
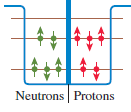
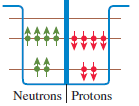
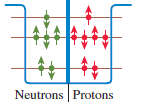
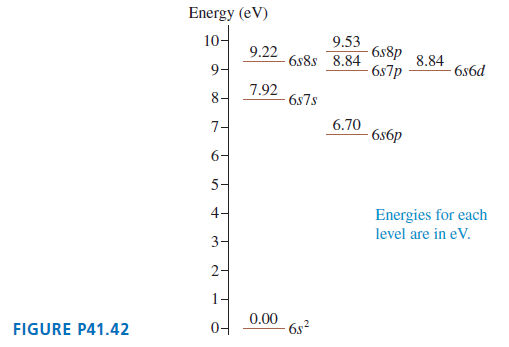
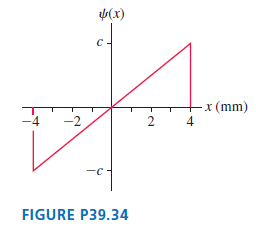
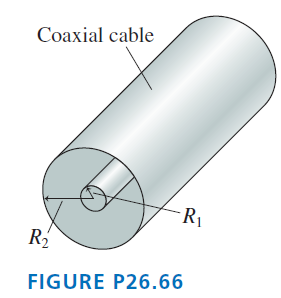
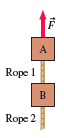
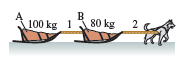
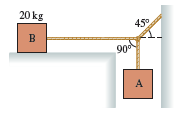
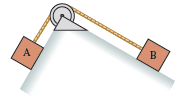
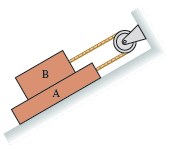
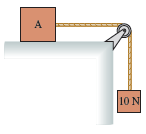
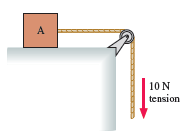
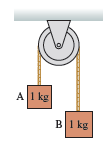
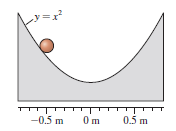
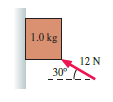
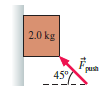
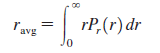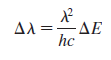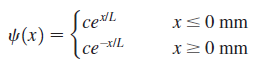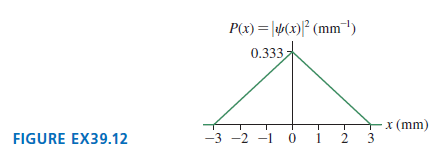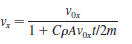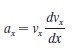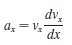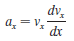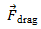Physics for Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics 4th edition Randall D. Knight - Solutions
Discover the ultimate resource for mastering "Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics, 4th Edition" by Randall D. Knight. Access comprehensive answers key and solutions pdf to enhance your understanding of complex topics. Our online platform offers solved problems, detailed chapter solutions, and step-by-step answers to ensure clarity in learning. Dive into our extensive test bank and instructor manual to prepare effectively for exams. Ideal for students and educators alike, our textbook solutions are available for free download, providing an invaluable tool for academic success.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()