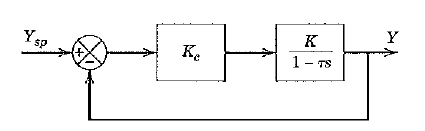
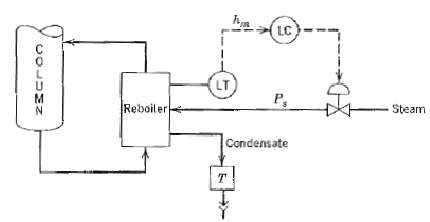
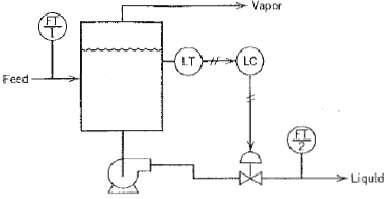
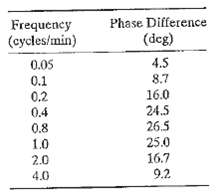
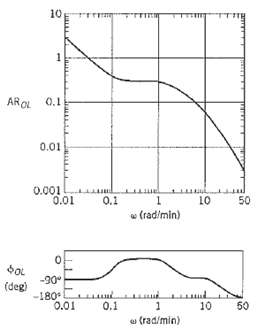
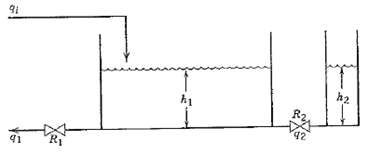
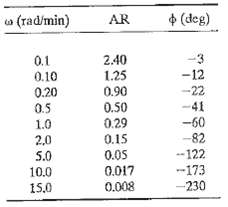
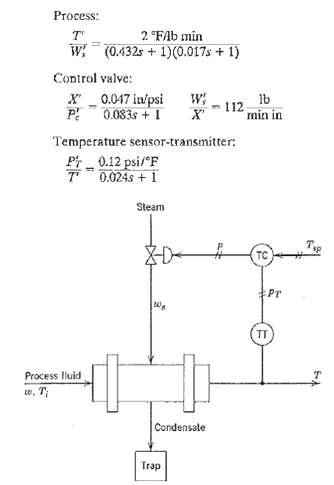
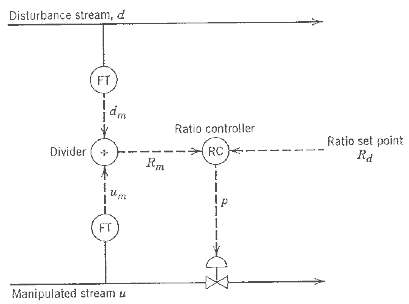
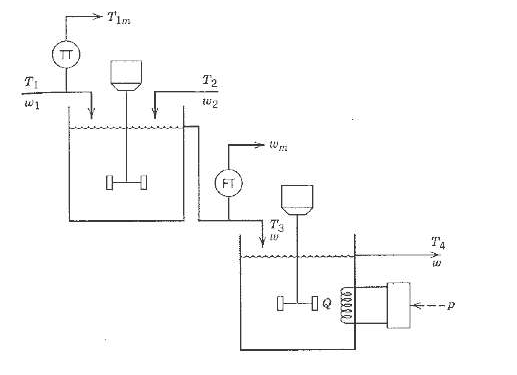
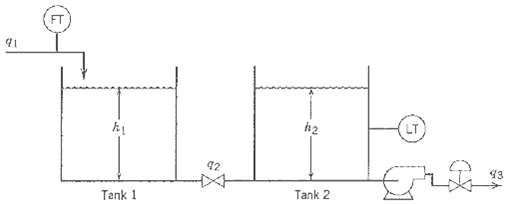
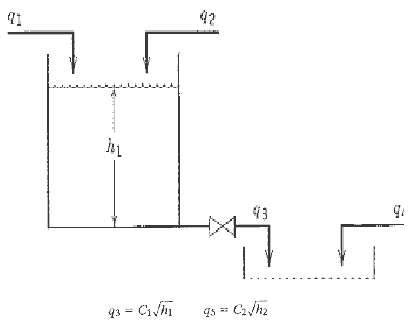
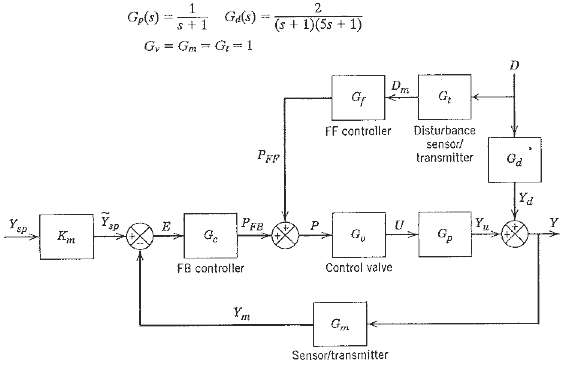
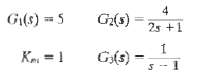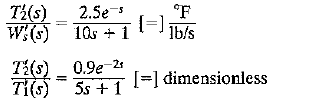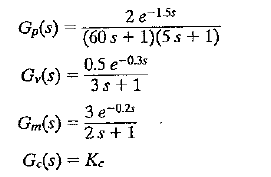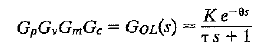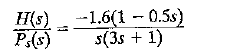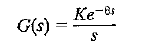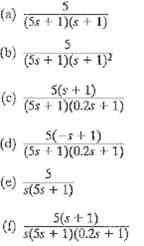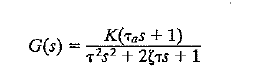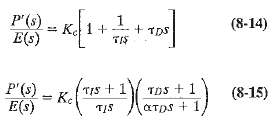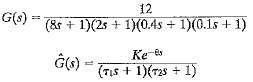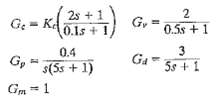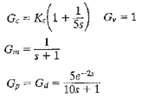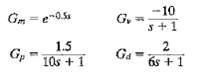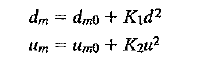![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()



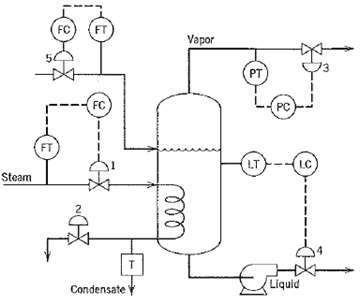

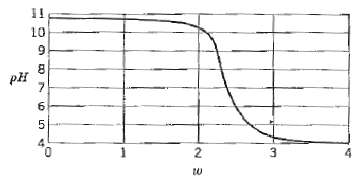


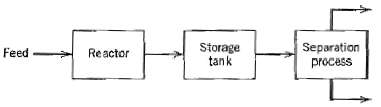
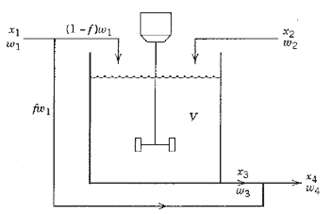
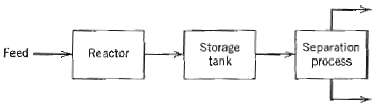
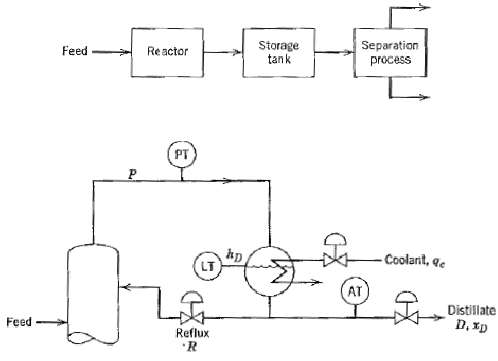
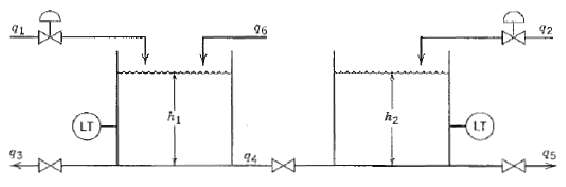
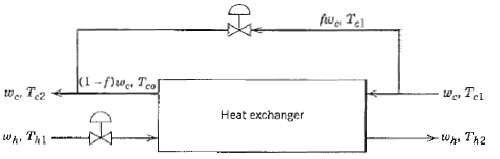
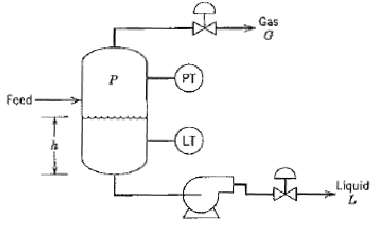
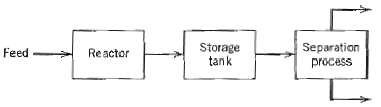
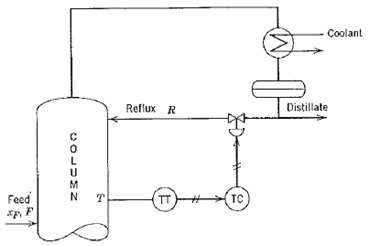
![T'(s) K2 та E(s) (mA] туря) P(s) [psi] PAs) Kip Гpsi] P'(s) K, K. [°F1 Кл, [mAI TS + 1 (°F) ImA] 의사품 т](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1553/6/8/6/3385c9b5f42837f81553686338709.jpg)