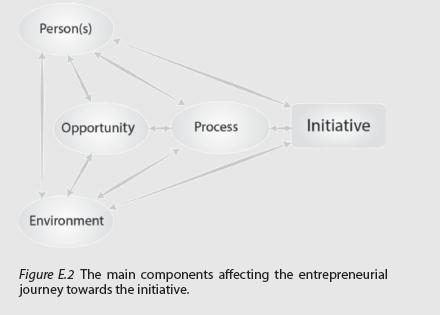
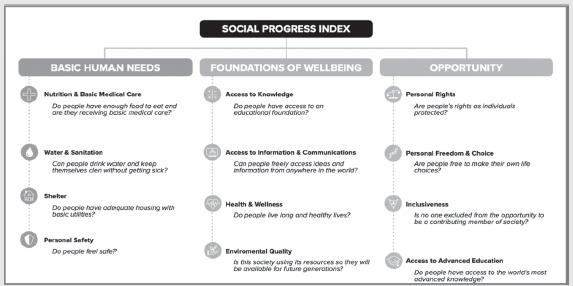
Entrepreneurial Small Business 3rd Edition Jerry Katz, Jerome A Katz - Solutions
Unlock the full potential of your entrepreneurial skills with the "Entrepreneurial Small Business 3rd Edition" by Jerry Katz and Jerome A Katz. Our comprehensive solutions and answers key are designed to guide you through the textbook's challenging questions and answers. Dive into detailed chapter solutions and test bank materials, available for free download. Our step-by-step answers and solution manual ensure you have access to expertly solved problems, making learning seamless. Whether you're an instructor seeking an instructor manual or a student looking for solutions in PDF format, our resources provide unmatched support.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()